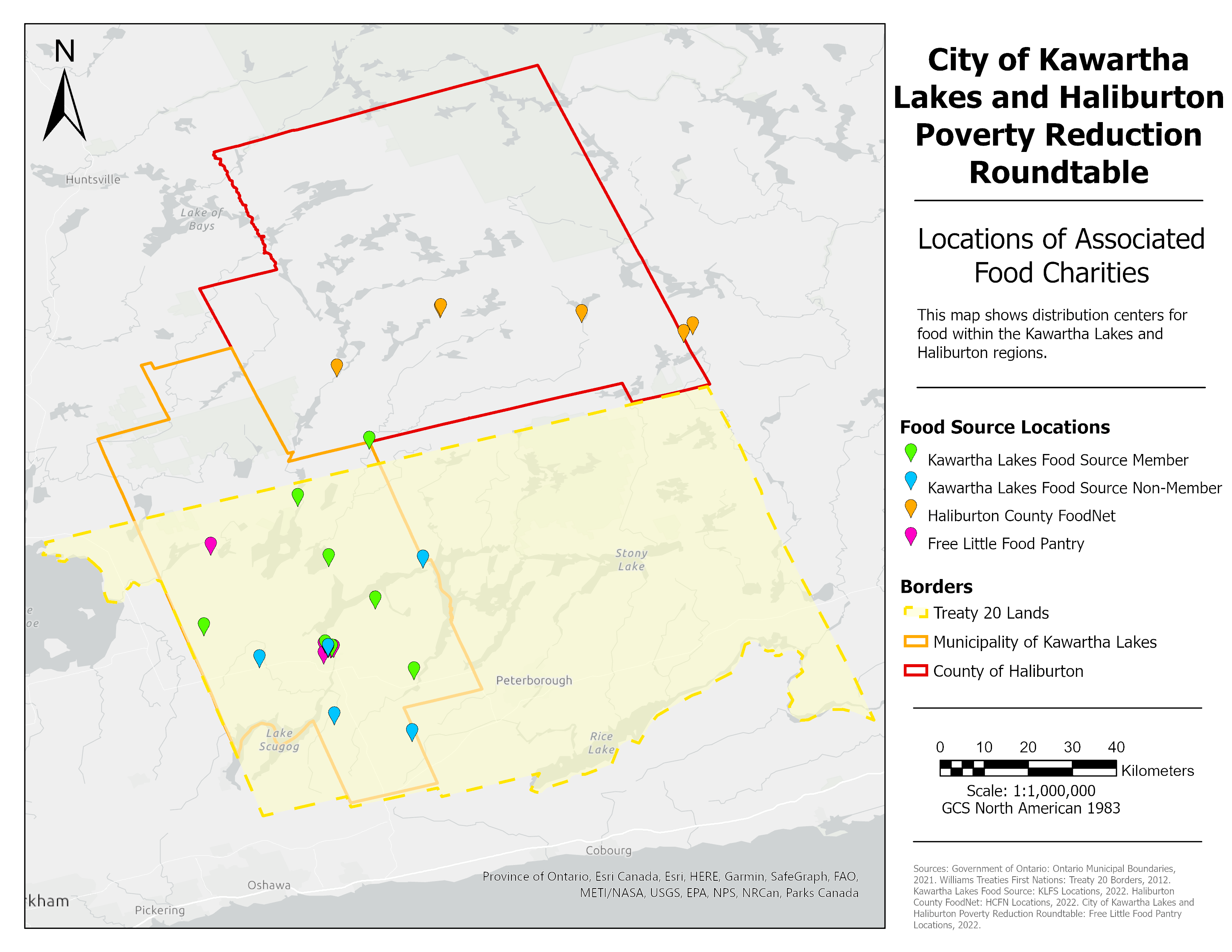
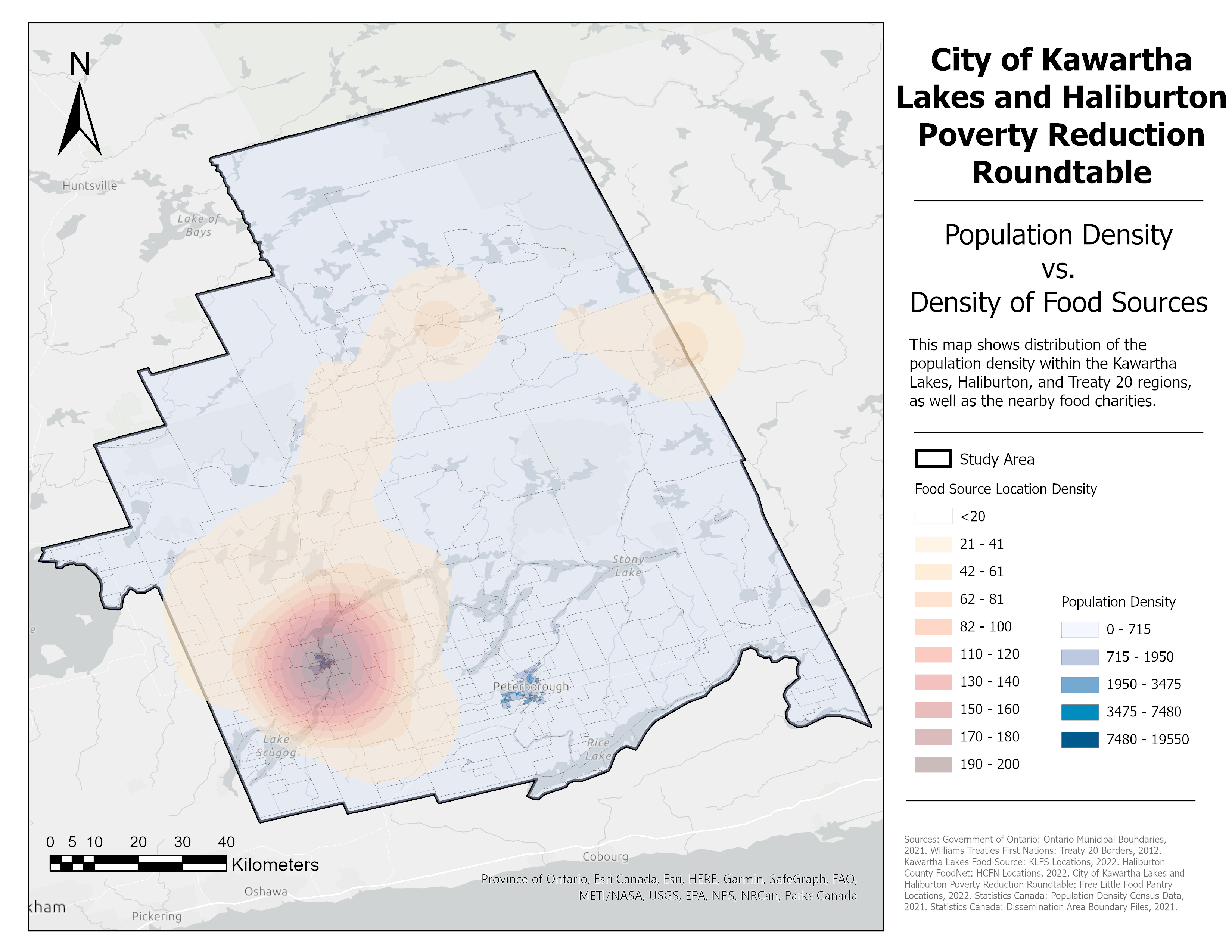
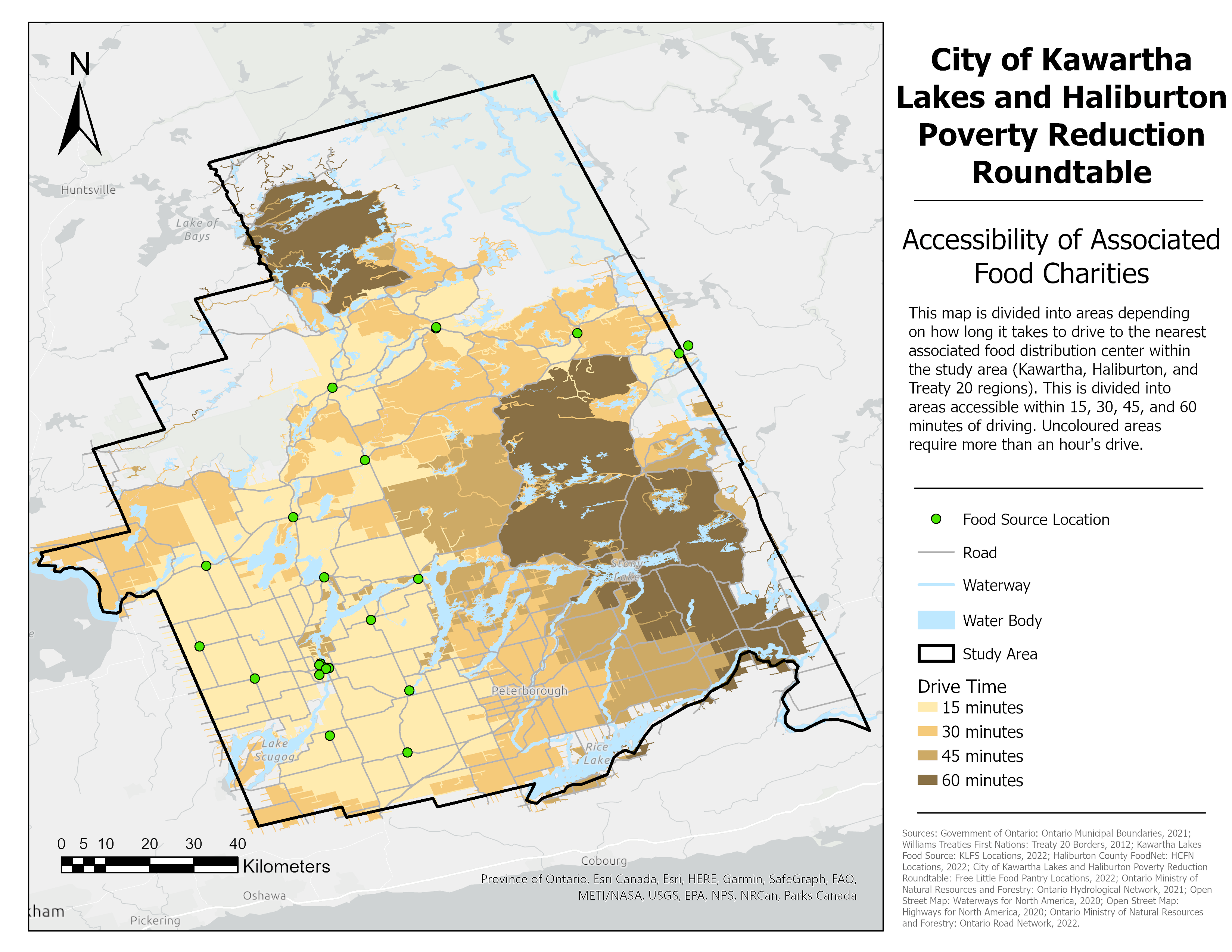
Spatial Analysis
The food charities associated with the program were separated into four different categories: Kawartha Lakes Food Source Member & Non-Member, Haliburton County FoodNet and Free Little Food Pantry. While the food sources are evenly distributed in the Municipality of Kawartha Lakes, they are more sparsely distributed in the Country of Haliburton. While the areas are not densely populated, the food sources are not dispersed in the same pattern as the population, resulting in uneven per-capita availability. Overall, only 72.86% of the study area is within a 60 minute drive of a food source.